Sustainable AI: The Future of Technology
- Puneet Sharma, Vice President of Insurance Technology, WITS Innovation Lab
- Jan 20, 2025
- 3 min read
Introduction: The Promise and Pitfalls of AI
Artificial Intelligence (AI) has been the backbone of transformative advancements across industries, reshaping healthcare, finance, manufacturing, and more. With the promise of optimizing processes, reducing operational inefficiencies, and delivering personalized experiences, AI is at the forefront of innovation.
However, as the scale and scope of AI expand, so does its environmental footprint. High-energy consumption for training large models, reliance on fossil-fueled data centers, and the demand for powerful hardware all contribute to the growing carbon emissions problem. As a society, we are now tasked with answering a crucial question: How can we make AI sustainable while continuing to push the boundaries of what’s technologically possible?
The Environmental Impact of AI
AI is undeniably resource-intensive. To contextualize the impact, let’s take a closer look at how training large AI models like GPT or BERT affects the environment.
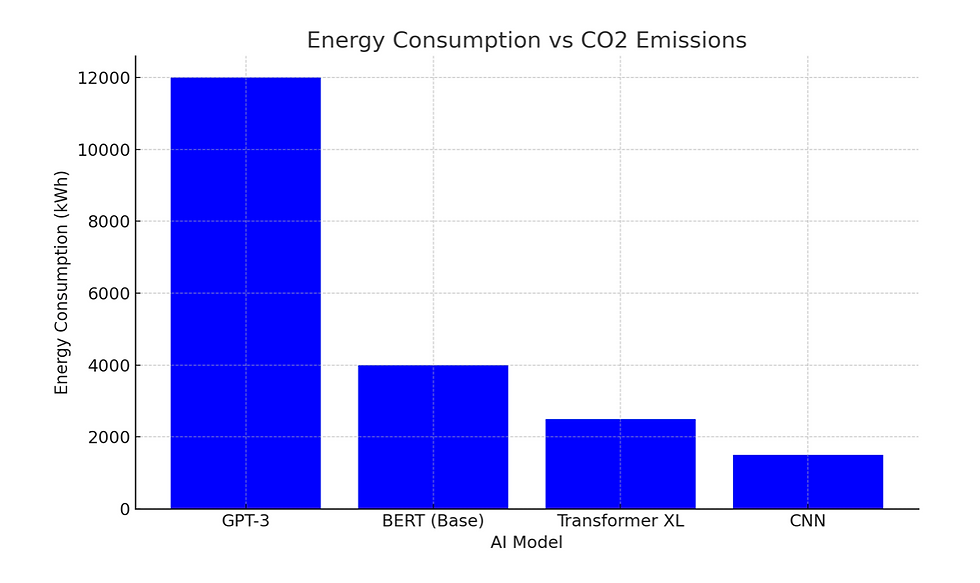
Training AI models requires massive computational resources. A study conducted by the University of Massachusetts Amherst revealed that training a single large AI model can emit nearly 626,000 pounds of CO2—equivalent to the lifetime emissions of five cars. Below is a graphical representation of the energy costs of training various AI models.
AI Hardware: A Double-Edged Sword
In addition to the energy costs of training and running AI models, the hardware needed to support AI-driven processes also leaves an environmental footprint. The mining of rare earth minerals, production of semiconductors, and disposal of outdated hardware all contribute to the carbon cost of AI.
Investing in more energy-efficient hardware, promoting reuse and recycling of AI infrastructure, and exploring alternatives such as quantum computing can potentially reduce these negative impacts.
Key Strategies for Achieving Sustainable AI
With these environmental challenges in mind, AI must evolve. The following strategies focus on creating sustainable AI infrastructures and approaches to minimize environmental impact while maintaining technological advancements.
1. Energy-Efficient Algorithms
Developing energy-efficient algorithms is an essential step toward minimizing AI’s carbon footprint. Traditional AI models, such as deep learning networks, require extensive computing power due to large datasets and resource-heavy training processes. This approach can be optimized by:
Pruning techniques: Reducing the size of the AI model without sacrificing accuracy.
Quantization: Lowering the precision of numbers in neural networks, reducing the computational load.
Knowledge Distillation: Creating smaller, more efficient models that mimic the behavior of larger ones.
2. Green Data Centers
Data centers are integral to AI’s computational backbone, but their energy demands make them a significant source of greenhouse gas emissions. To mitigate this, green data centers are emerging as a solution. These centers leverage renewable energy, innovative cooling techniques, and efficient power management to minimize environmental impact.
Case Study: Microsoft’s Project Natick
Microsoft’s Project Natick is a prime example of innovation in green data centers. Launched as an underwater data center, it uses seawater for natural cooling and operates on renewable energy sources such as wind and tidal power. Early reports suggest that this approach not only reduces energy consumption but also increases operational reliability.
3. AI in Edge Computing
Edge computing brings AI processing closer to the data source, reducing latency and decreasing the amount of data transferred to the cloud. This decentralized approach can drastically cut the energy consumption associated with large-scale AI models, particularly in IoT ecosystems.
The Future of Sustainable AI
The push towards Sustainable AI will require collaboration across industries, researchers, and policymakers. The following trends and innovations are shaping the future of Sustainable AI:
Developing carbon-neutral AI models that utilize renewable energy sources.
Harnessing quantum computing to exponentially reduce the energy requirements for complex AI tasks.
Scaling the adoption of green data centers and promoting energy-efficient AI architectures.
The Role of Thought Leadership
As thought leaders, we have a responsibility to:
Advocate for Policy Changes:We must push for government policies that incentivize sustainable AI development and encourage the adoption of green data center practices.
Promote Research and Innovation: Supporting research into energy-efficient algorithms and sustainable AI infrastructure is crucial. This includes exploring emerging fields like neuromorphic computing, which mimics the energy efficiency of the human brain.
Foster Collaboration: We must create platforms for collaboration between technology companies, researchers, policymakers, and environmental organizations to collectively address the sustainability challenges of AI.
Conclusion: Leading the Way to Sustainable AI
The journey towards Sustainable AI is challenging, but not impossible. By focusing on energy-efficient algorithms, investing in green data centers, and exploring decentralized computing solutions, we can build a future where AI innovations are not only transformative but also environmentally conscious.
Author: Puneet Sharma, Vice President of Insurance Technology, WITS Innovation Lab
Disclaimer: The opinions expressed within this article are the personal opinions of the author. The facts and opinions appearing in the article do not reflect the views of IIA and IIA does not assume any responsibility or liability for the same.



